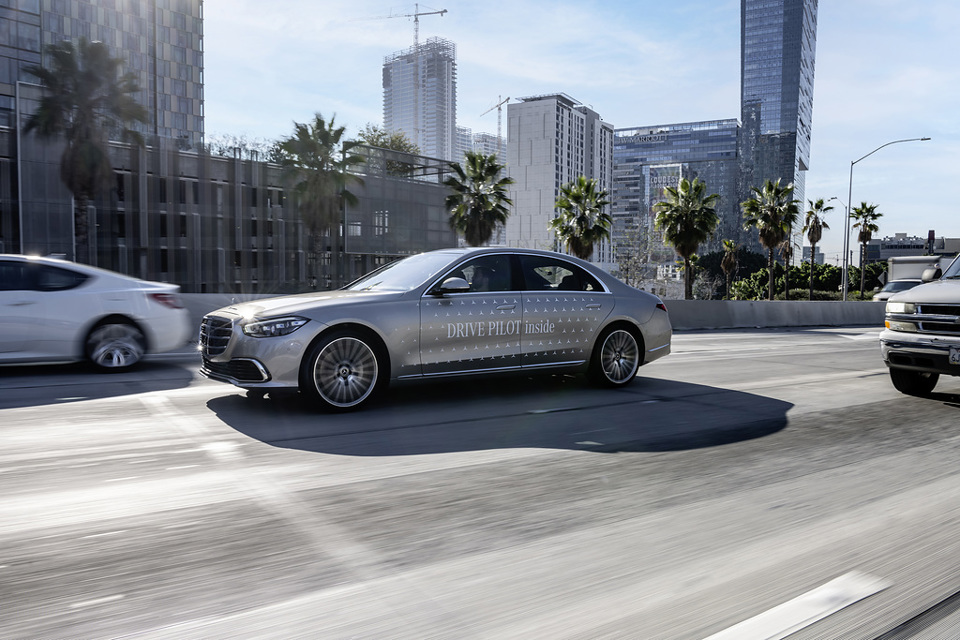
Mercedes-Benz will accept legal responsibility for collisions that occur in its cars fitted with a new Level 3 Automated Lane Keeping System.
Its new Drive Pilot system has been approved for us on German highways and can control the cars steering, acceleration and brakes at speed up to 40mph.
The car maker said it will accept liability in cases where the crash was caused by a fault with its technology, but not when the driver has "failed to comply with their duty of care".
Drive Pilot will be initially offered on the S-Class and EQS, as an option, in German Markets. Mercedes also plans to introduce the technology in US markets, once it gains approval.
Matthew Avery, chief research strategy officer at Thatcham Research, said: “The issue of liability in automated vehicles is complex and nuanced. It’s too crude to suggest that the carmaker should be liable in all circumstances; there will be times when an accident is and isn’t the carmaker’s responsibility.
“What is apparent in the case of Mercedes, the first to have approval – albeit in Germany – for technology that will allow drivers to disengage and do other things, is that when the automated system is in control, the carmaker will be liable.
“What’s less straightforward is an accident that occurs when the driver has failed “to comply with their duty of care”, for example when refusing to retake control of the car when prompted.
“It will be incumbent on carmakers to ensure drivers of their cars are confident, comfortable and have a strong grasp of their legal responsibilities – which in the UK would be in accordance with the Road Traffic Act. Absolute clarity is required for drivers in terms of their legal obligations behind the wheel and their understanding of how the system operates, especially during a handover from system to driver.
“This is challenged by the fact that a driver can take a long time to come back ‘into the loop’ after extended periods of effectively being chauffeured by the system.
“Insurance claims will require scrutiny, so the provision of data to help insurers understand who was in control of the vehicle at the time of an accident, system or driver, will also be vital.
“Trust will diminish if confusion reigns and drawn-out legal cases become common, hampering adoption of the technology and the realisation of its many societal benefits.”
The Law Commission of England and Wales and the Scottish Law Commission have published a joint report, making recommendations for the safe and responsible introduction of self-driving vehicles.
Under the Law Commissions’ proposals, when a car is authorised by a regulatory agency as having “self-driving features” and those features are in-use, the person in the driving seat would no longer be responsible for how the car drives. Instead, the company or body that obtained the authorisation - typically the vehicle manufacturer should face regulatory sanctions if anything goes wrong.
The report recommends introducing a new Automated Vehicles Act, to regulate vehicles that can drive themselves and suggests that a clear distinction should be made between features which just assist drivers, such as adaptive cruise control, and those that are self-driving.
Thatcham Research is currently leading the development of a consumer safety rating to support the safe adoption of Automated Driving Systems. Funded by government organisation Zenzic and in co-operation with Connected and Automated Mobility (CAM) Testbed partners, the rating will give UK motorists and insurers greater clarity around relative performance and safe use of automated technology.






















Login to comment
Comments
No comments have been made yet.